|
When a metal is subjected to a load (force), it is distorted or
deformed, no matter how strong the metal or light the load.
If the load is
small, the distortion will probably disappear when the load is removed. The
intensity, or degree, of distortion is known as strain. If the distortion
disappears and the metal returns to its original dimensions upon removal of the
load, the strain is called elastic strain. If the distortion disappears
and the metal remains distorted, the strain type is called plastic strain.
Strain will be discussed in more detail in the next chapter. When a load is
applied to metal, the atomic structure itself is strained, being compressed,
warped or extended in the process. The atoms comprising a metal are arranged in
a certain geometric pattern, specific for that particular metal or alloy, and
are maintained in that pattern by interatomic forces. When so arranged, the
atoms are in their state of minimum energy and tend to remain in that
arrangement. Work must be done on the metal (that is, energy must be added) to
distort the atomic pattern. (Work is equal to force times the distance the force
moves.)
Stress is the internal resistance, or counterforce, of a
material to the distorting effects of an external force or load. These
counterforces tend to return the atoms to their normal positions. The total
resistance developed is equal to the external load. This resistance is known as
stress.
Although it is impossible to measure the intensity of this
stress, the external load and the area to which it is applied can be measured.
Stress (s) can be equated to the load per unit area or the force (F) applied per
cross-sectional area (A) perpendicular to the force as shown in the Equation
below
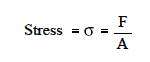
Where:
s = stress (psi or lbs of force per in.2)
F = applied force (lbs of force)
A = cross-sectional area (in.2)
Types of Stress
Stresses occur in any material that is subject to a load or any
applied force. There are many types of stresses, but they can all be generally
classified in one of six categories: residual stresses, structural stresses,
pressure stresses, flow stresses, thermal stresses, and fatigue stresses.
Residual Stress
Residual stresses are due to the manufacturing processes that
leave stresses in a material. Welding leaves residual stresses in the metals
welded.
Structural Stress
Structural stresses are stresses produced in structural
members because of the weights they support. The weights provide the loadings.
These stresses are found in building foundations and frameworks, as well as in
machinery parts.
Pressure Stress
Pressure stresses are stresses induced in vessels containing
pressurized materials. The loading is provided by the same force producing the
pressure.
Flow Stress
Flow stresses occur when a mass of flowing fluid induces a
dynamic pressure on a conduit wall. The force of the fluid striking the wall
acts as the load. This type of stress may be applied in an unsteady fashion when
flow rates fluctuate. Water hammer is an example of a transient flow stress.
Thermal Stress
Thermal stresses exist whenever temperature gradients are
present in a material. Different temperatures produce different expansions and
subject materials to internal stress. This type of stress is particularly
noticeable in mechanisms operating at high temperatures that are cooled by a
cold fluid.
Fatigue Stress
Fatigue stresses are due to cyclic application of a stress. The
stresses could be due to vibration or thermal cycling.
The importance of all stresses is increased when the materials
supporting them are flawed. Flaws tend to add additional stress to a material.
Also, when loadings are cyclic or unsteady, stresses can effect a material more
severely. The additional stresses associated with flaws and cyclic loading may
exceed the stress necessary for a material to fail. Stress intensity within the
body of a component is expressed as one of three basic types of internal load.
They are known as tensile, compressive, and shear. Figure 1 illustrates the
different types of stress.
Mathematically, there are only two types
of internal load because tensile and compressive stress may be regarded as the
positive and negative versions of the same type of normal loading.
However, in mechanical design, the response of components to the
two conditions can be so different that it is better, and safer, to regard them
as separate types.
As illustrated in Figure 1, the plane of a tensile or
compressive stress lies perpendicular to the axis of operation of the force from
which it originates. The plane of a shear stress lies in the plane of the force
system from which it originates. It is essential to keep these differences quite
clear both in mind and mode of expression.
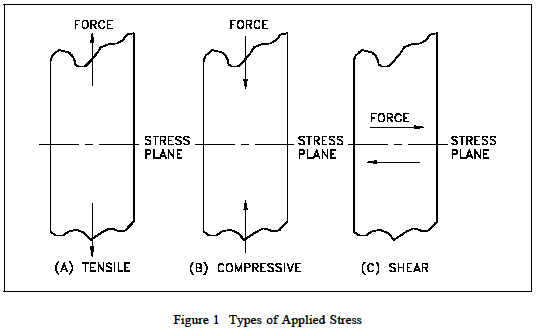
Tensile Stress
Tensile stress is that type of stress in which the two sections
of material on either side of a stress plane tend to pull apart or elongate as
illustrated in Figure 1(a).
Compressive Stress
Compressive stress is the reverse of tensile stress. Adjacent
parts of the material tend to press against each other through a typical stress
plane as illustrated in Figure 1(b).
Shear Stress
Shear stress exists when two parts of a material tend to slide
across each other in any typical plane of shear upon application of force
parallel to that plane as illustrated in Figure 1(c).
Assessment of mechanical properties is made by addressing the
three basic stress types. Because tensile and compressive loads produce stresses
that act across a plane, in a direction perpendicular (normal) to the plane,
tensile and compressive stresses are called normal stresses.
The shorthand designations are as follows.
For tensile stresses: "+SN" (or "SN") or
"s" (sigma)
For compressive stresses: "-SN" or "-s" (minus sigma)
The ability of a material to react to compressive stress or
pressure is called compressibility. For example, metals and liquids are
incompressible, but gases and vapors are compressible. The shear stress is equal
to the force divided by the area of the face parallel to the direction in which
the force acts, as shown in Figure 1(c) above.
Two types of stress can be present simultaneously in one plane,
provided that one of the stresses is shear stress. Under certain conditions,
different basic stress type combinations may be simultaneously present in the
material. An example would be a reactor vessel during operation. The wall has
tensile stress at various locations due to the temperature and pressure of the
fluid acting on the wall. Compressive stress is applied from the outside at
other locations on the wall due to outside pressure, temperature, and
constriction of the supports associated with the vessel. In this situation, the
tensile and compressive stresses are considered principal stresses. If present,
shear stress will act at a 45� angle to the principal stress.
|

