| Thermocouple |
Temperature
Sensor - The Thermocouple
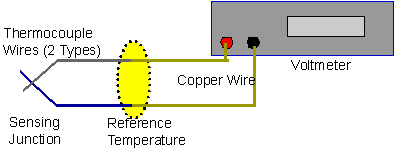
A thermocouple is a junction formed from two dissimilar metals. Actually,
it is a pair of junctions. One at a reference temperature (like 0
oC) and the other junction at the temperature to be measured.
A temperature difference will cause a voltage to be developed that is
temperature dependent. (That voltage is caused by something called the
Seebeck effect.) Thermocouples are widely used for temperature measurement
because they are inexpensive, rugged and reliable, and they can be used over a
wide temperature range. In particular, other temperature sensors (like
thermistors and LM35 sensors) are useful around room temperature, but the
thermocouple can
The
Thermocouple
-
When you use a thermocouple,
you need to ensure that the connections are at some standard temperature, or you
need to use an electronically compensated system that takes those voltages into
account. If your thermocouple is connected to a data acquisition system,
then chances are good that you have an electronically compensated system.
Let us look at some other types of
base-metal thermocouples. Type T thermocouples are widely used as are type
K and Type N.
-
Type K (Ni-Cr/Ni-Al)
thermocouples are also widely used in the industry. It has high thermopower and
good resistance to oxidation. The operating temperature range of a Type K
thermocouple is from -269 oC to +1260 oC. However, this
thermocouple performs rather poorly in reducing atmospheres.
-
Type T (Cu/Cu-Ni) thermocouples
can be used in oxidizing of inert atmospheres over the temperature range of -250
oC to +850 oC. In reducing or mildly oxidizing environments, it
is possible to use the thermocouple up to nearly +1000
oC.
-
Type N (Nicrosil/Nisil)
thermocouples are designed to be used in industrial environments of temperatures
up to +1200
oC.
A
polynomial equation used to convert thermocouple voltage to temperature (oC)
over a wide range of temperatures. We can write the polynomial as:
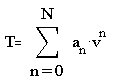
The coefficients, an are
tabulated in many places. Here are the NBS polynomial coefficients
for a type K thermocouple. (Source: T. J. Quinn, Temperature , Academic
Press Inc.,1990)
|
Type K
Polynomial Coefficients
|
|
|
n
|
an
|
|
0
|
0.226584602
|
|
1
|
24152.10900
|
|
2
|
67233.4248
|
|
3
|
2210340.682
|
|
4
|
-860963914.9
|
|
5
|
4.83506x1010
|
|
6
|
-1.18452x1012
|
|
7
|
1.38690x1013
|
|
8
|
-6.33708x1013
|
What If
The Surrounding Temperature Exceeds Limits?
There
are really no thermocouples that can withstand oxidizing atmospheres for
temperatures above the upper limit of the platinum-rhodium type thermocouples.
We cannot, therefore, measure temperature in such high temperature conditions.
Other options for measuring extremely high temperatures are radiation or the
noise pyrometer. For non-oxidizing atmospheres, tungsten-rhenium based
thermocouples shows good performance up to +2750 oC. They can be used, for a
short period, in temperatures up to +3000 oC.
The
selection of the types of thermocouple used for low temperature sensing is
primarily based on materials of a thermocouple. In addition, thermopower at low
temperatue is rather low, so measurement of EMF will be proportionally small as
well.
More Facts
On Various Thermocouple Types
-
A variety of thermocouples
today cover a range of temperature from -250 oC to +3000
oC. The different types of thermocouple are given letter
designations: B, E, J, K, R, S, T and N
-
Types R,S and B are noble metal
thermocouples that are used to measure high temperature. Within their
temperature range, they can operate for a longer period of time under an
oxidizing environment.
-
Type S and type R thermocouples
are made up of platinum (Pt) and rhodium (Rh) mixed in different ratios. A
specific Pt/Rh ratio is used because it leads to more stable and reproducible
measurements. Types S and R have an upper temperature limit of +1200 oC
in oxidizing atmospheres, assuming a wire diameter of 0.5mm.
-
Type S and type R thermocouples
are made up of platinum (Pt) and rhodium (Rh) mixed in different ratios. A
specific Pt/Rh ratio is used because it leads to more stable and reproducible
measurements. Types S and R have an upper temperature limit of +1200 oC
in oxidizing atmospheres, assuming a wire diameter of 0.5mm.
-
Type B thermocouples have a
different Pt/Rh ratio than Type S and R. It has an upper temperature limit of
+1750 oC in oxidizing atmospheres. Due to an increased amount of
rhodium content, type B thermocouples are no quite so stable as either the Type
R or Type S.
-
Types E, J, K, T, and N are
base-metal thermocouples that are used for sensing lower temperatures. They
cannot be used for sensing high temperatures because of their relatively low
melting point and slower failure due to oxidation.
-
Type B thermocouples have a
different Pt/Rh ratio than Type S and R. It has an upper temperature limit of
+1750 oC in oxidizing atmospheres. Due to an increased amount
of rhodium content, type B thermocouples are no quite so stable as either the
Type R or Type S. we will look into some differences between different
base-metal thermocouples.
-
Type E (Ni-Cr/Cu-Ni)
thermocouples have an operating temperature range
from -250 oC to +800 oC. Their use is
less widespread than other base-metal thermocouples due to its low operating
temperature. However, measurements made by a Type E have a smaller margin of
error. 1000 hours of operation in air of a Type E thermocouple at +760
oC, having 3mm wires, shold not lead to a change in EMF equivalent to
more than +1 oC.
-
Type J (Fe/Cu-Ni) thermocouples
are widely used in industry due to their high thermopower and low cost. This
type of thermocouple has an operating temperature range from 0 oC
to +760 oC.
|

