Radio receiver dynamic range
- overview or tutorial of the basics of radio receiver dynamic range
performance used for specifying the performance of radio receivers used in radio
communications systems.
Sensitivity is one of the main specifications of any radio
receiver. However the sensitivity of a set is by no means the whole story. The
specification for a set may show it to have an exceedingly good level of
sensitivity, but when it is connected to an antenna its performance may be very
disappointing because it is easily overloaded when strong signals are present,
and this may impair its ability to receive weak signals. In today's radio
communications environment where there are very many transmitters close by and
further away, good levels of sensitivity are needed along with the ability to
handle strong signals both on and off channel and the dynamic range of the radio
receiver is very important.
The overall dynamic range of the receiver is very important
because it is just as important for a set to be able to handle strong signals
well as it is to be able to pick up weak ones. This becomes very important when
trying to pick up weak signals in the presence of nearby strong ones. Under
these circumstances a set with a poor dynamic range may not be able to hear the
weak stations picked up by a less sensitive set with a better dynamic range.
Problems like blocking, inter-modulation distortion and the like within the
receiver may mask out the weak signals, despite the set having a very good level
of sensitivity. These parameters are obviously important when determining what
equipment should be used in a radio communications system.
What is dynamic range?
The dynamic range of a radio receiver is essentially the
range of signal levels over which it can operate. The low end of the range is
governed by its sensitivity whilst at the high end it is governed by its
overload or strong signal handling performance. Specifications generally use
figures based on either the inter-modulation performance or the blocking
performance. Unfortunately it is not always possible to compare one set with
another because dynamic range like many other parameters can be quoted in a
number of ways. However to gain an idea of exactly what the dynamic range of a
radio receiver means it is worth looking at the ways in which the measurements
are made to determine the range of the radio receiver.
Sensitivity
The first specification to investigate is the sensitivity
of a set. The main limiting factor in any radio receiver is the noise generated.
For most applications either the signal to noise ratio or the noise figure is
used as described in a previous issue of MT. However for dynamic range
specifications a figure called the minimum discernible signal (MDS) is often
used. This is normally taken as a signal equal in strength to the noise level.
As the noise level is dependent upon the bandwidth used, this also has to be
mentioned in the specification. Normally the level of the level of the MDS is
given in dBm i.e. dB relative to a milliwatt and typical values are around -135
dBm in a 3 kHz bandwidth.
Strong signal handling
Although the sensitivity is important the way in which a
radio receiver handles strong signals is also very important. Here the overload
performance governs how well the receiver performance.
In the ideal world the output of an RF amplifier would be
proportional to the input for all signal levels. However RF amplifiers only have
a limited output capability and it is found that beyond a certain level the
output falls below the required level because it cannot handle the large levels
required of it. This gives a characteristic like that shown below. From this it
can be seen that RF amplifiers are linear for the lower part of the
characteristic, but as the output stages are unable to handle the higher power
levels the signals starts to become compressed as seen by the curve in the
characteristic.
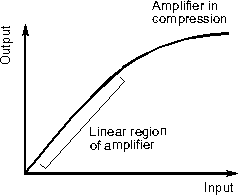
A typical amplifier characteristic
The fact that the RF amplifier is non-linear does not
create a major problem in itself. However the side effects do. When a signal is
passed through a non-linear element there are two main effects which are
noticed. The first is that harmonics are generated. Fortunately these are
unlikely to cause a major problem. For a harmonic to fall near the frequency
being received, a signal at half the received frequency must enter the RF
amplifier. The front end tuning should reduce this by a sufficient degree for it
not to be a noticeable problem under most circumstances.
The other problem that can be noticed is that signals mix
together to form unwanted products. These again are unlikely to cause a problem
because any signals which could mix together should be removed sufficiently by
the front end tuning. Instead problems occur when harmonics of in-band signals
mix together.
Third order products
Problems occur when harmonics of in-band signals mix
together. It is found that a comb of signals can be produced as shown below, and
these may just fall on the same frequency as a weak and interesting station,
thereby masking it out so it cannot be heard.
It is simple to calculate the frequencies where the
spurious signals will fall. If the input frequencies are f1 and f2,
then the new frequencies produced will be at 2f1 - f2, 3f1
- 2f2, 4f1 - 3f2 and so forth. On the other
side of the two main or original signals products are produced at 2f2
- f1, 3f2 - 2f2, 4f2 - 3f1
and so forth as shown in the diagram. These are known as odd order
inter-modulation products. Two times one signal plus one times another makes a
third order product, three times one plus two times another is a fifth order
product and so forth. It can be seen from the diagram that the signals either
side of the main signals are first the third order product, then fifth, seventh
and so forth.
To take an example with some real figures. If large
signals appear at frequencies of 30.0 MHz and 30.01 MHz, then the
inter-modulation products will appear at 30.02, 30.03, 30.4 ...MHz and 29.99,
29.98, 29.97 ..... MHz.
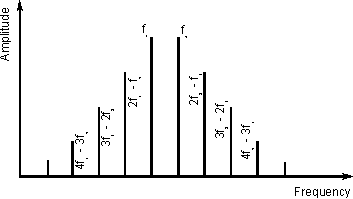
Inter-modulation products
Radio receiver blocking
Another problem that can occur when a strong signal is
present is known as blocking. As the name implies it is possible for a strong
signal to block or at least reduce the sensitivity of a radio receiver. The
effect can be noticed when listening to a relatively weak station and a nearby
transmitter starts to radiate, and the wanted signal reduces in strength. The
effect is caused when the front-end RF amplifier starts to run into compression.
When this occurs the strongest signal tends to "capture" the RF amplifier
reducing the strength of the other signals. The effect is the same as the
capture effect associated with FM signals.
The amount of blocking is obviously dependent upon the
level of the signal. It also depends on how far off channel the strong signal
is. The further away, the more it will be reduced by the front end tuning and
the less the effect will be. Normally blocking is quoted as the level of the
unwanted signal at a given offset (normally 20 kHz) to give a 3 dB reduction in
gain.
Dynamic range definition
When looking at dynamic range specifications, care must be
taken when interpreting them. The MDS at the low signal end should be viewed
carefully, but the limiting factors at the top end show a much greater variation
tin the way they are specified. Where blocking is used a reduction of 3 dB
sensitivity is normally specified, but in some cases may be 1 dB used. Where the
inter-modulation products are chosen as the limiting point the input signal
level for them to be the same as the MDS is often taken. However whatever
specification is given, care should be taken to interpret the figures as they
may be subtlety different in the way they are measured from one receiver to the
next.
To gain a feel for the figures which may be obtained where
inter-modulation is the limiting factor figures of between 80 and 90 dB range
are typical, and where blocking is the limiting factor figures around 115 dB are
generally achieved in a good radio receiver used for professional radio
communications applications.
Designing for optimum performance
It is not an easy task to design a highly sensitive radio
receiver that also has a wide dynamic range. However this is an important
requirement for many radio communications systems, particularly where mobile
radio communications units may come into close proximity with each other.
To achieve the required level of performance a number of
methods can be used. The front-end stage of the radio receiver is the most
critical in terms of noise performance. It should be optimised for noise
performance rather than gain. Input impedance matching is critical for this. It
is interesting to note that the optimum match does not correspond exactly with
the best noise performance. The amplifier should also have a relatively high
output capability to ensure it does not overload. The mixer is also critical to
the overload performance. To ensure the mixer is not overloaded there should not
be excessive gain preceding it. A high level mixer should also be used (i.e. one
designed to accept a high-level local oscillator signal). In this way it can
tolerate high input signals without degradation in performance. Care should be
taken in the later stages of the receiver to ensure that they can tolerate the
level of signals likely to be encountered. A good AGC system also helps prevent
overloading and the generation of unwanted spurious signals.
A radio receiver with a good dynamic range will be able to
give a far better account of itself under exacting conditions than one designed
purely for optimum sensitivity. With the exacting requirements needed for
today's radio communications systems where mobile radio communications means
that transmitters and receivers come into close proximity, good levels of
sensitivity are needed along with the ability of the radio receiver to tolerate
high signal levels, either on or off channel. Only when the radio receiver has a
good dynamic range will the required performance level for the whole radio
communications system be achieved.
|

