The Cytoplasm
Within the plasma membrane is the cytoplasm. It consists of a clear
jelly-like fluid called the a) cytosol or intracellular fluid in
which b) cell inclusions, c) organelles and d) microfilaments
and microtubules are found.
a) Cytosol
The cytosol consists mainly of water in which various molecules are dissolved
or suspended. These molecules include proteins, fats and carbohydrates as well
as sodium, potassium, calcium and chloride ions. Many of the reactions that take
place in the cell occur in the cytosol.
b) Cell inclusions
These are large particles of fat, glycogen and melanin that have been
produced by the cell. They are often large enough to be seen with the light
microscope. For example the cells of adipose tissue (as in the insulating fat
layer under the skin) contain fat that takes up most of the cell.
c) Organelles
Organelles are the �little organs� of the cell - like the heart,
kidney and liver are the organs of the body. They are structures with
characteristic appearances and specific �jobs� in the cell. Most can not be seen
with the light microscope and so it was only when the electron microscope was
developed that they were discovered. The main organelles in the cell are the
ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, Golgi complex and
lysosomes. A cell containing these organelles as seen with the electron
microscope is shown in diagram 3.3.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are tiny spherical organelles that make proteins by joining
amino acids together. Many ribosomes are found free in the cytosol, while others
are attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranes that form
channels throughout the cytoplasm from the nucleus to the plasma membrane.
Various molecules are made in the ER and transported around the cell in its
channels. There are two types of ER: smooth ER and rough ER.
-
- Smooth ER is where the fats in the cell are made and in some
cells, where chemicals like alcohol, pesticides and carcinogenic
molecules are inactivated.
-
- The Rough ER has ribosomes attached to its surface. The
function of the Rough ER is therefore to make proteins that are modified
stored and transported by the ER (Diagram 3.11).
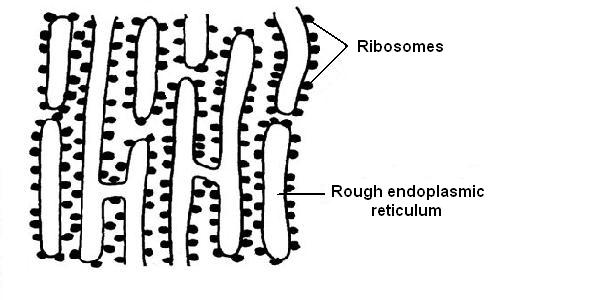
Diagram 3.11 - Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Mitochondria
Mitochondria (singular mitochondrion) are oval or rod shaped
organelles scattered throughout the cytoplasm. They consist of two membranes,
the inner one of which is folded to increase its surface area. (Diagram 3.12)
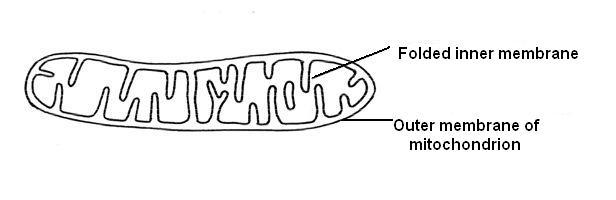
Diagram 3.12 - A mitochondrion
Mitochondria are the �power stations� of the cell. They make energy by �burning�
food molecules like glucose. This process is called cellular respiration.
The reaction requires oxygen and produces carbon dioxide which is a waste
product. The process is very complex and takes place in a large number of steps
but the overall word equation for cellular respiration is-
-
-
-
- Glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + energy
Note that cellular respiration is different from respiration or
breathing. Breathing is the means by which air is drawn into and expelled from
the lungs. Breathing is necessary to supply the cells with the oxygen required
by the mitochondria and to remove the carbon dioxide produced as a waste product
of cellular respiration.
Active cells like muscle, liver, kidney and sperm cells have large numbers of
mitochondria.
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi bodies in a cell together make up the Golgi apparatus.
Golgi bodies are found near the nucleus and consist of flattened membranes
stacked on top of each other rather like a pile of plates (see diagram 3.13).
The Golgi apparatus modifies and sorts the proteins and fats made by the ER,
then surrounds them in a membrane as vesicles so they can be moved to
other parts of the cell.
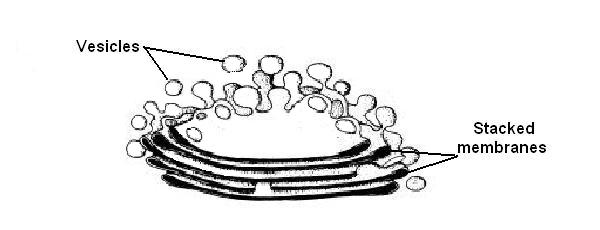
Diagram 3.13 - A Golgi body
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are large vesicles that contain digestive enzymes. These
break down bacteria and other substances that are brought into the cell by
phagocytosis or pinocytosis. They also digest worn-out or damaged organelles,
the components of which can then be recycled by the cell to make new structures.
d) Microfilaments And Microtubules
Some cells can move and change shape and organelles and chemicals are moved
around the cell. Threadlike structures called microfilaments and
microtubules that can contract are responsible for this movement.
These structures also form the projections from the plasma membrane known as
flagella (singular flagellum) as in the sperm tail, and cilia
found lining the respiratory tract and used to remove mucus that has trapped
dust particles (see chapter 4).
Microtubules also form the pair of cylindrical structures called
centrioles found near the nucleus. These help organise the spindle used in
cell division.
The Nucleus
The nucleus is the largest structure in a cell and can be seen with
the light microscope. It is a spherical or oval body that contains the
chromosomes. The nucleus controls the development and activity of the cell.
Most cells contain a nucleus although mature red blood cells have lost their's
during development and some muscle cells have several nuclei.
A double membrane similar in structure to the plasma membrane surrounds the
nucleus. Pores in this nuclear membrane allow communication between the nucleus
and the cytoplasm.
Within the nucleus one or more spherical bodies of darker material can be
seen, even with the light microscope. These are called nucleoli and are
made of RNA. Their role is to make new ribosomes.
Chromosomes
Inside the nucleus are the chromosomes which:
- contain DNA;
- control the activity of the cell;
- are transmitted from cell to cell when cells divide;
- are passed to a new individual when sex cells fuse together in sexual
reproduction.
In cells that are not dividing the chromosomes are very long and thin and
appear as dark grainy material. They become visible just before a cell divides
when they shorten and thicken and can then be counted (see diagram 3.14).
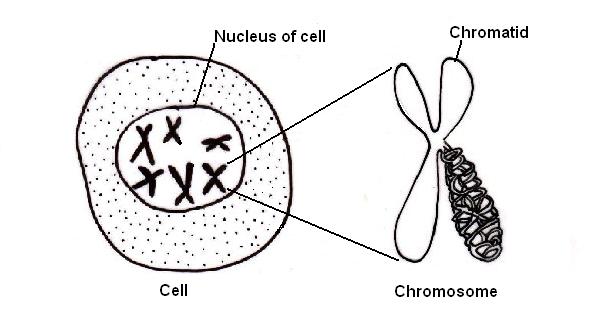
Diagram 3.14 - A cell with an enlarged chromosome
The number of chromosomes in the cells of different species varies but is
constant in the cells of any one species (e.g. horses have 64 chromosomes, cats
have 38 and humans 46). Chromosomes occur in pairs (i.e. 32 pairs in the horse
nucleus and 19 in that of the cat). Members of each pair are identical in length
and shape and if you look carefully at diagram 3.15, you may be able to see some
of the pairs in the human set of chromosomes.

Diagram 3.15 - A full set of human chromosomes
|

